The three kinds of web
The Internet is a huge worldwide network of servers, computers and devices that started in the 1970s. In 1989, Tim Berners-Lee, invented the World Wide Web (WWW) while working at CERN to meet the demand for automated information-sharing between scientists in universities and institutes around the world. The web has since become the dominant communication medium on the Internet, and today we talk of the emergence of Web 3.0. The web is often described as consisting of the surface web, the deep web, and the dark web. Let us see what they mean, and explore how the dark web works in a little more detail.
Surface web and deep web
The surface web, along with the deep web, is the part of the Internet most of us use every day such as facebook.com or kuenselonline.com. It’s accessible through regular browsers such as Google Chrome or Firefox.
Deep web refers to the part of the internet that is behind closed doors such as the pages and databases that are only meant for authorized users within an organization. For example, what you see on Amazon website as a customer is the surface web, but the complete database of items that an Amazon employee can see is part of the deep web. The private data and pages of companies, universities, libraries, hospitals, governments, international organizations, and so on also form part of the deep web. The deep web is by far the biggest part of the internet, estimated to make up between 90 and 95% of the complete world wide web.
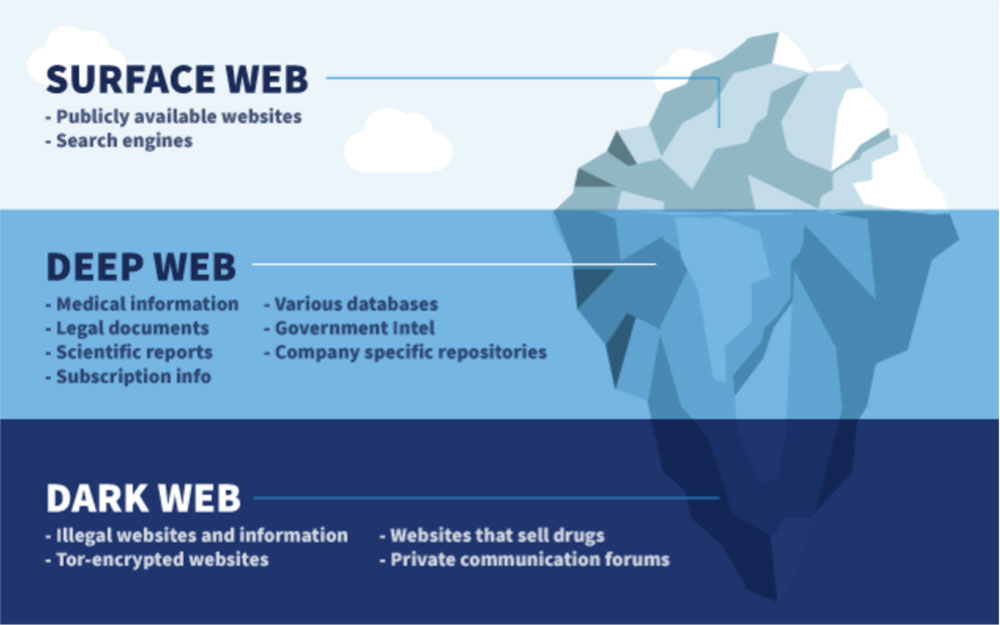
So, what is the “Dark Web” then?
Unlike the surface web and the deep web, the dark web is an unregulated hidden part of the Internet that’s only accessible through a special browser such as Tor browser. The dark web websites cannot be found using search engines like Google. Some people call the dark web as the deep web too, but they are not the same. The deep web is accessible through regular browsers as long as you have the exact URL and user credentials, but this is not the case for the dark web.
While there are other anonymous networks, Tor is the largest and most extensively used dark web network. No organization, business, or government is in charge of the dark web or is able to enforce rules. This is exactly the reason why the dark web is commonly associated with illegal activities.
The origins of the dark web
Tor began as an experimental project by the US Department of Defense back in 2002. “The government created the anonymized and encrypted Tor network, short for “The Onion Router”, to protect its communications with spies. The open-source platform quickly became popular giving rise to the dark web that we know of today. That anonymity provided by the network appealed to both privacy conscious individuals and criminals, and that is how it has gained notoriety as a platform for criminals. However, experts say that the dark web as a technology is just a neutral tool that affords anonymity to its users. The anonymity afforded is used for positive purposes by journalists and human rights activists, while it is used for criminal purpose by others.
How dark web operates
The dark web makes individual’s IP address difficult for anyone to trace by encrypting traffic in multiple layers and bouncing it through a network of random computers, each of which removes a layer of encryption before bouncing it on to the next device. Encrypting traffic in multiple layers is akin to the many layers of an onion. Hence, this project was called the “The Onion Router”.
Where are dark web websites hosted?
The Tor network works as a peer to peer connection presented over hidden services using special software that is freely available. It seems fairly easy for any one to set up a dark web website. The dark website can be hosted anywhere, even on the servers of normal webhosting service providers as long as they allow it. But they may be hosted on private servers so that the owner has full control over it. Dark web websites have URLs ending in .onion, not .com or .bt etc. For example, even BBC has a website on the dark web and its URL is http://bbcnewsd73hkzno2ini43t4gblxvycyac5aw4gnv7t2rccijh7745uqd.onion/
The dark web is not indexed by any search engine like Google. Hence, it cannot be searched. You need to know the specific website address (URL) to be able to visit it.
Is dark web dangerous to explore?
The dark web is used by criminals for illegal activities such as drug dealing, child pornography, terrorism, dealing in fire arms, hacking and selling user credentials such as credit card information etc. Therefore, it is not a place that one should venture into. Even on the open surface web, there are a lot of unscrupulous people on the look out for gullible victims to scam or dupe. There is no need to go into details on the dangers presented by the dark web to an unsuspecting user.
“The dark web doesn’t carry as many of the social contracts that website providers follow to protect users on the rest of the web. As such, users can find themselves regularly exposed to some types of malware like Keyloggers, Botnet malware, Ransomware, Phishing malware”, according to Cyber Security experts.
The dark web seems especially popular for hackers to sell user credentials that they have stolen from their victims. “The number of data breaches shows no signs of slowing down, resulting in vast swathes of exposed records and personal information available for purchase on the dark web. Recent studies identified that over 15 billion credentials are currently available there, and these transactions between hackers and cybercriminals continue to fuel more cyberattacks and breaches”, according to an expert.
As you may have guessed it, yes, the currency of choice for transactions on the dark web is cryptocurrencies, especially Bitcoin.
Future of dark web
“As the desire for privacy continues to grow, the dark web shows no sign of losing its appeal. In less than two decades, the network has gone from a discrete project supporting anonymous communications to a large unregulated network. What the future holds for the dark web is unclear, but it doesn’t look like it will disappear anytime soon,” according to an article on Forbes.com by Mike Wilson titled “Demystifying the dark web”.


